Friend or foe? MSU researchers explore ancient partnership between moss and fungi
Article Highlights
- In a new paper published in The Plant Journal, Björn Hamberger and Davis Mathieu analyzed
how mosses colonized habitats with and without fungi present, providing clues to how
plants managed to transition to land 450 million years ago.
- The researchers discovered that the extent of moss-fungi interactions often depends
on the presence of endobacteria within the fungi, revealing an intricate web of microscopic
relationships.
- This discovery raises exciting questions as to the complicated nature of moss-fungi partnerships and how plant life successfully conquered our planet.
No, not the patch of brown grasses peeking through a snowbank, or the acres of trees with their bare boughs and branches, waiting for spring.
Look down, and you’ll find the only green to see is right under your boot — a lush carpet of mosses.
For Björn Hamberger, a James K. Billman Jr., M.D., Endowed Professor in the College of Natural Science’s Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, this year-round toughness is cause for admiration on its own.

“It gives you an idea of just how resilient these organisms are, and it’s probably one of the reasons that mosses have stuck around and haven’t been lost through evolution,” Hamberger said.
But it’s also a starting point for research with a scope that spans eons — from ancient Earth to humanity’s future in space. Appearing in The Plant Journal, the Hamberger lab’s latest paper seeks to better understand how mosses and other plants conquered our planet, and how, in order to do so, may have gotten some much-needed help from their longtime collaborators fungi.
From early Earth to future Mars
Mosses made the transition to land 450 million years ago during the Ordovician period, a process that Hamberger suspects couldn’t have succeeded without some teamwork.
When mosses made landfall, they would’ve had to account for a host of new and challenging variables, including water regulation, gravity, fluctuating temperatures and exposure to UV light.
Thankfully, mosses encountered a landscape already colonized by early fungi whose root-like networks, or mycelium, could absorb critical nutrients from the earth. In exchange for these nutrients, early terrestrial plants provided the fungi with a carbon source, kickstarting a new relationship that’s endured until the current day.
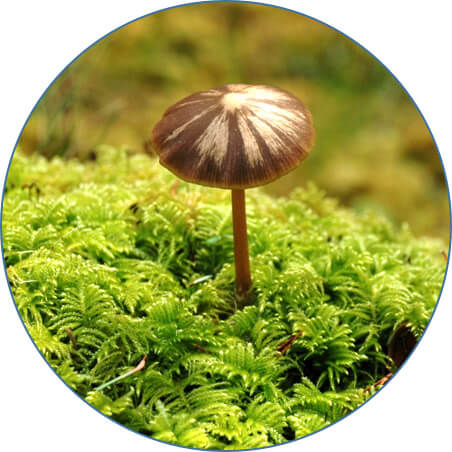

A mushroom coexisting with its mossy neighbor. At least 80% of modern plants coordinate with fungi, with these relationships helping plants grow stronger and become more resilient. Credit: Britta Hamberger
“At least 80% of modern plants still collaborate in some way with fungi, getting help to grow stronger and to become more resilient,” Hamberger explained. “As we look into a future where plants need to sustain a growing population, this will be a critical factor.”
Working with mosses for over a decade, Hamberger and his research group took part in a special exhibit at the Detroit Science Gallery called “Fog of Dawn” in 2019 that featured mosses growing in terrariums aimed at mimicking the ambience of primordial Earth and the subsequent takeover of plants and fungi.
The group also engineered moss to express foreign, modern land-plant biochemical pathways, producing products such as patchouli oil.
Here, Hamberger sees exciting potential in the realm of space exploration. Mosses and other plants could act as natural fabricators for building materials or medicines while converting carbon dioxide to oxygen during space flights.
“If you can bring plants with you on such a journey and give them the blueprints to create useful products, that will cut down on the immense weight of raw materials in orbit,” Hamberger said.
“Plus, when it comes to terraforming a place such as Mars, why not start with moss — a plant that’s successfully altered our own planet already?”
With their latest research in The Plant Journal, the Hamberger lab hopes to further pull back the curtain on plant-microbial interactions and discover the ways moss and fungi communicate at a microscopic level.

Friend or foe?
To accomplish these goals, Hamberger and Davis Mathieu, a doctoral student and first author of the paper, designed an experiment that would provide a front row seat to moss-fungi interactions in real-time.
Over three months, the lab observed the moss, Physcomitrium patens, colonize different terrariums. Some habitats were entirely without fungi, while others were cocultured with two species of the ground-dwelling fungi lineage, Mortirellaceae, which likely existed at the same time plants first began to conquer land.
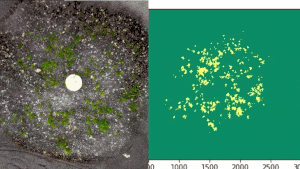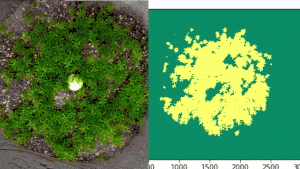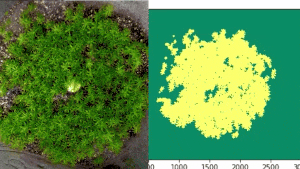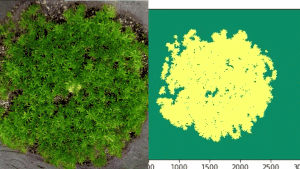
The fungi were provided by fungal and genetics expert Greg Bonito, associate professor in MSU’s Department of Plant, Soil and Microbial Sciences and a long-time collaborator of Hamberger.
Using microscopy, genetic analysis and Raspberry Pi microcomputers, the researchers tracked the subtle but distinct ways the moss interacted with its fungal neighbors. The team discovered that these interactions came to depend on a unique addition to the cast — endobacteria within the fungi.
These endobacteria provided a challenging question of their own. The endobacteria are completely dependent on their fungal host for survival, but it was unclear if they were bringing any value to the relationship.
“Generally, endobacteria are not seen as beneficial to fungi, with cells experiencing some big trade-offs for housing them,” said Mathieu. “This of course raises the question: why are they still around?”
Mathieu and others found that when endobacteria are present, fungi can more easily interact with their mossy neighbors. When experimenting with fungi that have their endobacteria removed, a complex web of relationships began to appear.
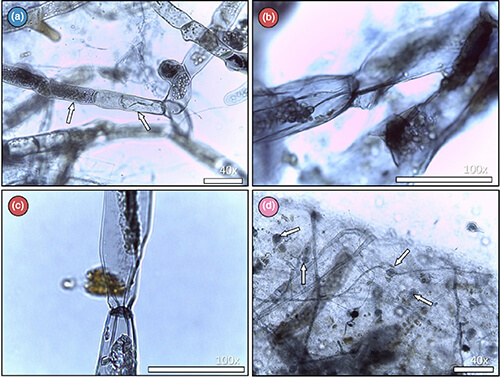
For instance, one species of fungi seemed to “eat” the moss from the inside when its endobacteria were present. But in samples where the endobacteria were absent?
“It lives side-by-side with the moss, totally indifferent,” Mathieu explained.
Meanwhile, another species of fungi that provided benefits to the moss changed its behavior when its endobacteria were removed. The fungi started producing spore-like structures indicative of stress and no longer colonized the moss as they once did.
The Hamberger lab is looking forward to further unraveling these friend-or-foe relationships between moss, fungi and endobacteria, and what these discoveries mean for understanding life on Earth.
“We thought we’d start with something simple and straightforward — the beginning of land plant life,” Hamberger said ironically. “But it turns out there’s this super exciting and very complex story that can teach us something about what happened during land plant evolution, what got us on this planet and what might get us to a different planet.”
He also hopes that this research might spur interest in crucial lifeforms we pass by every day, often without realizing it.
“Maybe it might inspire a little bit of appreciation for these cool organisms who can live under harsh conditions and are the first ones in spring to say, ‘Yay, let’s go,’ when the snow melts and the sunlight returns.”